Stream processing¶
On the DSH, you can use Apache Flink for real-time processing of data streams that you produce via MQTT or Apache Kafka:
- The DSH allows you to produce and consume a huge amount of data continuously via Apacha Kafka or MQTT.
- Apache Flink lets you process this continuous stream, using jobs and tasks that can run in parallel.
- The DSH offers Apache Flink as a platform service, with a fixed setup:
- Using Apache ZooKeeper, the DSH always enforces high availability to ensure that a Flink cluster will always continue executing your submitted jobs.
- If your process needs to remember the state of certain point of information (for example a counter), then Apache Flink stores this state and backs it up.
- Apache Flink uses an object storage bucket to save checkpoints and savepoints for the state of processes, and a volume to store JAR-packaged jobs.
Flink architecture¶
When you deploy a Flink as a service, then the DSH deploys the following components:
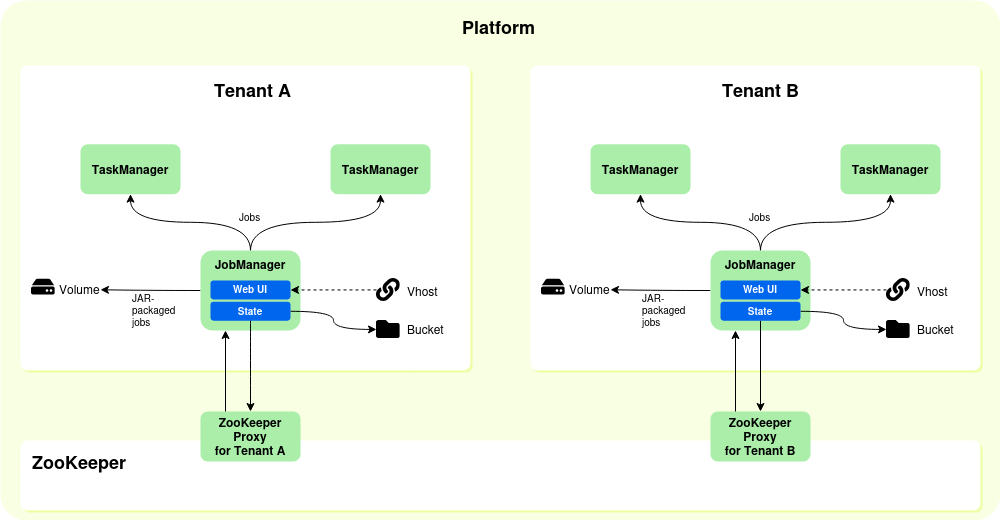
- A Flink JobManager, which distributes the jobs across the TaskManagers. You can set the allocated CPUs and memory of the JobManager when you deploy a Flink cluster.
- One or more Flink TaskManagers, which execute the jobs. You can set the number of instances when you deploy a Flink cluster, and the allocated CPUs and memory for each instance.
- A vhost, to access the Flink UI. In the Flink UI, you can submit jobs to the Flink cluster and check job statuses.
- An object storage bucket, to store state information and checkpoints.
- A volume, to store any JAR-packaged jobs that you submit to the Flink cluster. This ensures that these jobs are still available after a relaunch.
- A ZooKeeper proxy, to store state information and checkpoints for each tenant separately. The DSH uses ZooKeeper to ensure high availability for Flink clusters, and each DSH platform contains one instance of ZooKeeper for all its tenants. The ZooKeeper proxy prevents tenants from overwriting each other’s state information or checkpoints.
The table below displays the names of the components, and any default settings. Some components also have fixed settings, which you can’t change as a tenant:
| Component | Namespace inside tenant | Default settings |
|---|---|---|
| Flink JobManager | flink-cluster-jobmanager |
Default settings:
Fixed settings, see Flink configuration and Flink metric reporters for more information:
|
| Flink TaskManager | flink-cluster-taskmanager |
Default settings:
Fixed settings, see Flink configuration and Flink metric reporters for more information:/p>
|
| Vhost | flink-cluster-ui-<tenant-name> |
The URL for the vhost is https://flink-cluster-ui-<tenant-name>.<platform>.kpn-dsh.com |
| Volume | faas-volume |
The volume has a fixed size of 20 GiB. |
| ZooKeeper proxy | zookeeper-proxy |
The fixed address of the ZooKeeper proxy is Fixed settings:
|
| Object storage bucket | flink-cluster-bucket |
The address of the object storage bucket (or blob storage on Azure) depends on your platform. Inspect the object storage bucket in question to see its address. See Object storage bucket for more information. |
Note
By default, the DSH configures an object storage bucket as state backend for the JobManager. Apache Flink uses this state backend to persist job states across platform relaunches or cluster restarts.
However, flink-statebackend-rocksdb is also available on the DSH as a provided package. As a consequence, you can use RocksDB as state backend in your job directly, instead of the default object storage bucket.
If you destroy your Flink cluster, then the states in RocksDB are deleted. However, the DSH doesn’t delete the linked object storage bucket automatically when you destroy a Flink cluster. As a consequence, redeploying the Flink cluster restores the states of the Flink jobs from the bucket.
Dependencies¶
The table below lists the different packages that are part of DSH’s Flink as a service, and their versions for Apache Flink 1.12 and Apache Flink 1.15.
| Package | Organization | Version in Flink 1.12 | Version in Flink 1.15 |
|---|---|---|---|
| flink-runtime-web | org.apache.flink | 1.12.2 | 1.15.2 |
| flink-metrics-prometheus | org.apache.flink | 1.12.2 | 1.15.2 |
| flink-connector-kafka | org.apache.flink | 1.12.2 | 1.15.2 |
| flink-s3-fs-hadoop | org.apache.flink | 1.12.2 | 1.15.2 |
| flink-avro | org.apache.flink | 1.12.2 | 1.15.2 |
| flink-json | org.apache.flink | 1.12.2 | 1.15.2 |
| flink-metrics-dropwizard | org.apache.flink | 1.12.2 | 1.15.2 |
| flink-statebackend-rocksdb | org.apache.flink | 1.12.2 | 1.15.2 |
| flink-streaming-java | org.apache.flink | 1.12.2 | 1.15.2 |
| flink-streaming-scala | org.apache.flink | 1.12.2 | 1.15.2 |
| javax.xml.bind | jaxb-api | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 |
Tip
See Running your own jobs to discover how you should deal with the dependecies if you add your own jobs to the Flink cluster.
Managing Flink as a service¶
This section describes how you can deploy, access and destroy a Flink cluster.
Deploying a Flink cluster¶
Take the following steps to deploy Apache Flink in your tenant:
- Click “Services” > “Overview” in the menu bar of the DSH Console.
- At the top of the overview page, click the “+ Flink Cluster” button.
- Fill out the fields:
- Flink version: Select the version of Apache Flink that you want to deploy.
- Zone: Select the DSN zone in which to deploy the Flink cluster.
- Under “JobManager”:
- CPUs: Enter the number of CPUs, expressed in cores, that the DSH should allocate to the Flink JobManager. The minimum value is “0.3”.
- Memory: Enter the amount of memory, expressed in MB, that the DSH should allocate to the Flink JobManager. The minimum value is “1024”.
- Under “TaskManager”:
- CPUs: Enter the number of CPUs, expressed in cores, that the DSH should allocate to the Flink TaskManagers. The minimum value is “0.3”.
- Memory: Enter the amount of memory, expressed in MB, that the DSH should allocate to the Flink JobManager. The minimum value is “1024”, and the default value is “3072”.
- Instances: Enter the number of instances for Flinks’s Taskmanagers. If you enter 2, or a higher value, then you will be able to execute tasks in parallel. The minimum value is “1”, and the default value is “2”.
- Click “Deploy Flink Cluster”.
Accessing the Flink UI¶
Take the following steps to access the Flink UI:
- Click “Services” > “Overview” in the menu bar of the DSH Console.
- In the list of services, click “Flink Cluster”.
- Click the “Flink UI” button.
Running your own jobs¶
If you create your own jobs to run on the cluster of Flink as a service, then you need to bear the following in mind:
- The builds of Flink as a service are made with Scala 2.12.8, and they run on Java 11 JRE in the Docker containers.
- Your jobs need to comply with the dependencies. Mark the latter as “provided” in your own project build, and include them explicitly in the JAR that you use for job assembly.
- The DSH uses the
slf4jlogging system, in thelogback-classicimplementation:- All your jobs must use this logging system.
- The log configuration is part of the Docker containers and makes logging possible in the Flink UI and in the task logs of the individual services.
- The DSH excludes all packages from
log4j,slf4j-log4j12, andlog4j-over-slf4j.
Destroying a Flink cluster¶
Take the following steps to destroy a Flink cluster:
- Click “Services” > “Overview” in the menu bar of the DSH Console.
- In the list of services, click “Flink Cluster”.
- Click the “Destroy Flink Cluster” button, and “Yes, destroy” to confirm.
Warning
- The DSH deletes the Flink cluster, but it doesn’t destroy the linked ZooKeeper proxy and the object storage bucket. The DSH merely makes them inaccessible to your tenant.
- If you deploy the Flink cluster again at a later time, then the DSH uses the existing ZooKeeper proxy and object storage bucket.
- As a consequence, redeploying a Flink cluster restores the states of the Flink jobs.