Database as a Service¶
Even though the DSH is a primarily a platform for streaming data, your service may still need a database to store data. The DSH offers the following database as a service (DBaaS) solution:
- The DBaaS uses YugabyteDB 2.11.1, which is compatible with PostgreSQL 11.2.
- YugabyteDB is a distributed database: it distributes all data across multiple tablets, and replicates these tablets on multiple tablet servers.
- The DSH deploys instances for the YugabyteDB tablet servers, stores the data in volumes, and uses an object storage bucket for backups.
- The DSH enforces TLS for the data in transit, and encrypts the volumes of the DBaaS.
- The DBaaS supports the following PostgreSQL extensions:
- You can deploy Pgweb from the App Catalog, wich allows you to explore the database in a browser.
Note
The DSH and YugabyteDB don’t support every feature of PostgreSQL. See Limitations for more information.
Architecture¶
If you create a DBaaS, the DSH deploys it using the setup below:
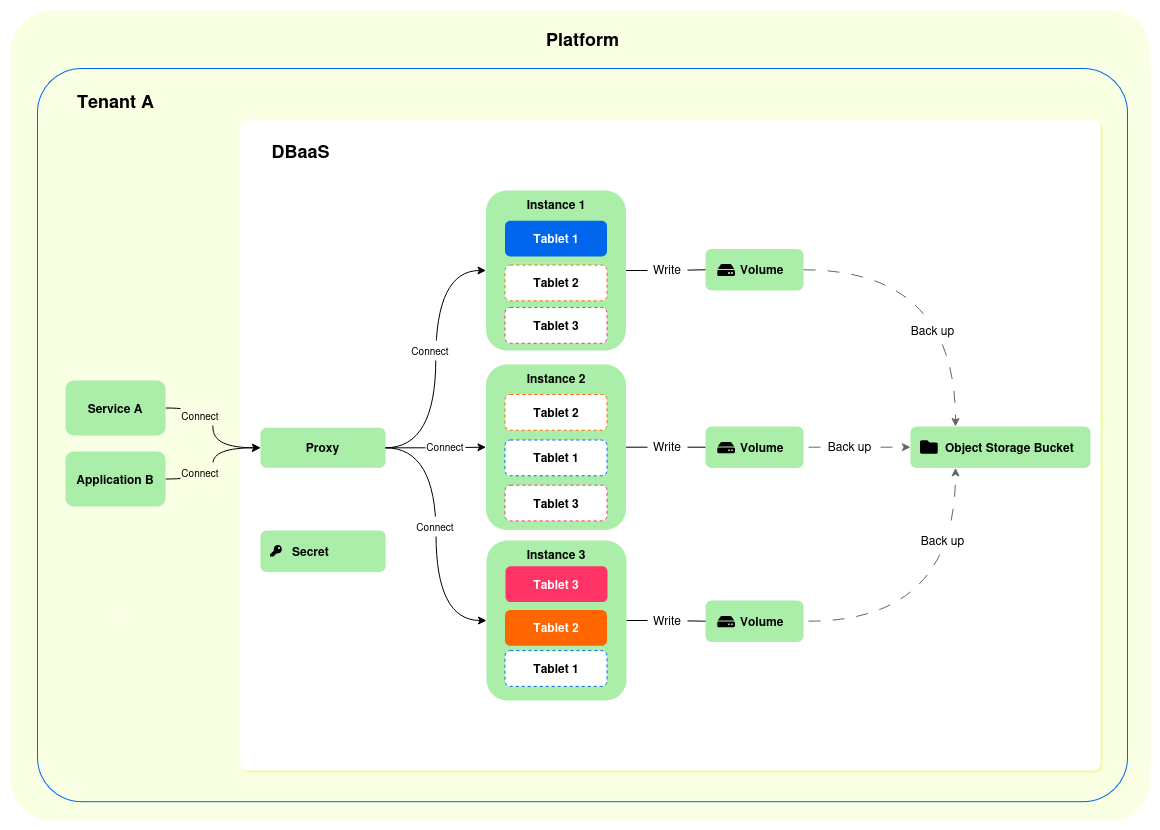
- A proxy service through which you can connect to the database, on port 5432, using a standard PostgreSQL driver. The proxy service has 0.1 CPU cores and 256 MB of memory allocated.
- A DSH secret for the connection password.
- A number instances for the YugabyteDB tablet servers:
- You can choose the number of instances when you create the DBaaS, but 3 instances is the minimum.
- YugabyteDB divides all data across multiple tablets.
- YugabyteDB applies a replication factor of 3 for the tablets.
- Every instance has an encrypted volume, and you can set its size when you create the DBaaS.
- The DSH backs up the contents of the volumes to an object storage bucket every 30 minutes.
Tip
When you deploy the DBaaS, make sure that the volumes are large enough for the database’s intended use:
- Once the volumes exist, you can’t increase their size.
- To prevent data corruption, the DSH sets the database to read-only mode once the disks are over the 95 % threshold.
Managing a DBaaS¶
This section describes how you can deploy, access and destroy a DBaaS.
Deploying a DBaaS¶
Take the following steps to deploy a DBaaS in your tenant:
- Click “Services” > “App Catalog” in the menu bar of the DSH Console.
- Click “SQL Database”.
- At the top of the page, click the version that you want to deploy, and then click the “Configure & Deploy” button.
-
Fill out the following fields:
-
App name: Enter the name that you want to use for the DBaaS. The name must have the following form:
- It must start with a lowercase letter.
- It can contain only lowercase letters (a–z) or numbers (0–9).
- It can’t be longer than 16 characters.
The app name isn’t the same as the PostgreSQL role, database, or tablespace created in the process: the DSH generates a unique name for them.
-
CPU: Enter the number of CPU cores per YugabyteDB tablet server:
- Each instance in the DBaaS represents a tablet server.
- The minimum value is 0.3 cores per instance for a database that receives a light load.
- It is recommended that you allocate 1.0–6.0 cores per instance for optimal performance.
- Extensions: Enter a comma-separated list of extensions that you want to add to the DBaaS. The available extensions are:
- Instances: Enter the number of instances that you want to deploy. Each instance represents a YugabyteDB tablet server. The minimum number of instances is 3, because that is the replication factor that YugabyteDB applies to tablets.
- Memory: Enter the amount of memory, in MB, for each instance:
- Each instance in the DBaaS represents a tablet server.
- The minimum value is 2048 MB (2 GB) per instance for a database that receives a light load, and that doesn’t have a PostGIS extension.
- It is recommended that you allocate at least 3072 MB for optimal performance.
- Volume_size: Enter the disk space, in GB, for each YugabyteDB tablet server:
- The minimum disk space per volume is 5 GB.
- In order to define the disk space, you have to take the replication factor of 3 into account, and the number of instances. Use the following formula:
(estimated_size * replication_factor) / number_of_instances. - For example, if you estimate that your database will never exceed the size of 20 GB, and you have 4 instances, then this will result in a disk space of 15 GB per volume:
(20 * 3) / 4 = 15. - You can’t resize the volumes once they are created, and the database stops working if the volumes are full.
- Snapshot_interval: This field has been deprecated, because the DSH automatically makes a backup every 30 minutes.
- Click “Deploy” to schedule the DBaaS for deployment.
-
Accessing a DBaaS¶
The DSH offers different ways to connect to your DBaaS:
- You can insert the DBaaS into the service definition of your service, which will make the hostname, database, username and application available inside your service. See Inserting a DBaaS for more information.
- You can deploy Pgweb from the App Catalog to access and navigate the DBaaS from your browser. See App Catalog for more information.
Tip
The DSH uses the standard PostgreSQL port 5432.
Destroying a DBaaS¶
Take the following steps to destroy an existing DBaaS:
- Click “Services” > “Overview” in the menu bar of the DSH Console.
- In the overview page, click the name of your DBaaS.
- In the details page of the DBaaS, click the “Manage DBaaS” button.
- Click the “Destroy DBaaS” button, and then “Yes, destroy” to confirm.
Limitations¶
The DBaaS comes with several limitations on PostgreSQL statements because DSH prohibits them, or because YugabyteDB 2.11.1 doesn’t support them.
Known issues¶
Take the following issues into account when you use the DBaaS on the DSH:
- YugabyteDB 2.11.1 doesn’t support the
GINandGISTmethods in the PostGIS extension. - The database stops working when its volumes are full.
- The DSH platform puts an upper limit on the CPU and memory of each service, including database instances:
- If you need more CPU or memory settings, then you can deploy more instances.
- For example, if you deploy a database with 8 CPUs or 30 GB of memory per instance, it won’t get scheduled.
- Instead, you can deploy a database with more instances, for example 8 instances with 3 GB of memory instead of 3 instances with 8 GB of memory.
Prohibited statements¶
The DSH prohibits the following PostgreSQL statements:
CREATE, ALTER, DROP TABLESPACEALTER DATABASE … RENAME TO …ALTER DATABASE … OWNER TO …ALTER DATABASE … WITH CONNECTION_LIMITALTER DATABASE … WITH IS_TEMPLATEALTER DATABASE … SET TABLESPACEALTER TABLE … SET TABLESPACEALTER MATERIALIZED VIEW … SET TABLESPACECREATE TABLE … TABLESPACE pg_defaultCREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW … TABLESPACE pg_defaultALTER INDEX ALL IN TABLESPACE … SET TABLESPACE …SECURITY LABEL … ON TABLESPACE …COMMENT ON TABLESPACE …GRANT … ON TABLESPACE …DROP EXTENSION dsh
For the statements below, you can configure only a limited set of paramaters:
| Statement | Permitted parameters |
|---|---|
|
DateStyle, IntervalStyle, TimeZone, array_nulls, backslash_quote, bytea_output, check_function_bodies, client_encoding, client_min_messages, default_transaction_isolation, extra_float_digit, search_path, and xmloption
|
SET/RESET
|
DateStyle, IntervalStyle, TimeZone, application_name, array_nulls, backslash_quote, bytea_output, check_function_bodies, client_encoding, client_min_messages, default_transaction_isolation, default_with_oids, extra_float_digit, lock_timeout, role, search_path, standard_conforming_strings, statement_timeout, and xmloption
|
Unsupported statements¶
YugabyteDB 2.11.1 doesn’t support the PostgreSQL statements below:
ALTER:ALTER AGGREGATE aggregate_with_argtypes RENAME TO nameALTER AGGREGATE aggregate_with_argtypes SET SCHEMA nameALTER COLLATION any_name REFRESH VERSIONALTER COLLATION any_name RENAME TO nameALTER COLLATION any_name SET SCHEMA nameALTER CONVERSION any_name RENAME TO nameALTER CONVERSION any_name SET SCHEMA nameALTER DATABASE any_name SET TABLESPACEALTER DOMAIN any_name ADD TableConstraintALTER DOMAIN any_name DROP CONSTRAINT [ IF EXISTS ] name opt_drop_behaviorALTER DOMAIN any_name DROP NOT NULLALTER DOMAIN any_name SET NOT NULLALTER DOMAIN any_name SET SCHEMA nameALTER DOMAIN any_name VALIDATE CONSTRAINT any_nameALTER DOMAIN_P any_name RENAME CONSTRAINT name TO nameALTER INDEX [ IF EXISTS ] qualified_name alter_table_cmdsALTER INDEX [ IF EXISTS ] qualified_name RENAME TO nameALTER INDEX ALL IN TABLESPACE name OWNED BY role_list SET TABLESPACE name opt_nowaitALTER INDEX ALL IN TABLESPACE name SET TABLESPACE name opt_nowaitALTER INDEX qualified_name DEPENDS ON EXTENSION nameALTER INDEX qualified_name index_partition_cmdALTER MATERIALIZED VIEW [ IF EXISTS ] qualified_name alter_table_cmdsALTER MATERIALIZED VIEW [ IF EXISTS ] qualified_name RENAME opt_column name TO nameALTER MATERIALIZED VIEW [ IF EXISTS ] qualified_name RENAME TO nameALTER MATERIALIZED VIEW ALL IN TABLESPACE name OWNED BY role_list SET TABLESPACE name opt_nowaitALTER MATERIALIZED VIEW ALL IN TABLESPACE name SET TABLESPACE name opt_nowaitALTER MATERIALIZED VIEW qualified_name DEPENDS ON EXTENSION nameALTER MATERIALIZED VIEW qualified_name SET SCHEMA nameALTER OPERATOR CLASS any_name USING access_method RENAME TO nameALTER OPERATOR CLASS any_name USING access_method SET SCHEMA nameALTER opt_procedural LANGUAGE name RENAME TO nameALTER PROCEDURE function_with_argtypes alterfunc_opt_list opt_restrictALTER PROCEDURE function_with_argtypes DEPENDS ON EXTENSION nameALTER PROCEDURE function_with_argtypes RENAME TO nameALTER PROCEDURE function_with_argtypes SET SCHEMA nameALTER PUBLICATION any_nameALTER PUBLICATION any_name ADD TABLEALTER PUBLICATION any_name DROP TABLEALTER PUBLICATION any_name SET TABLEALTER PUBLICATION name RENAME TO nameALTER ROUTINE function_with_argtypes alterfunc_opt_list opt_restrictALTER ROUTINE function_with_argtypes DEPENDS ON EXTENSION nameALTER ROUTINE function_with_argtypes RENAME TO nameALTER ROUTINE function_with_argtypes SET SCHEMA nameALTER RULE name ON qualified_name RENAME TO nameALTER SEQUENCE [ IF EXISTS ] qualified_name RENAME TO nameALTER SEQUENCE [ IF EXISTS ] qualified_name SET SCHEMA nameALTER SEQUENCE IF_P EXISTS qualified_name alter_table_cmdsALTER SEQUENCE qualified_name alter_table_cmdsALTER STATISTICS any_name RENAME TO nameALTER STATISTICS any_name SET SCHEMA nameALTER SUBSCRIPTION any_name CONNECTION SconstALTER SUBSCRIPTION any_name DISABLEALTER SUBSCRIPTION any_name ENABLEALTER SUBSCRIPTION any_name REFRESH PUBLICATION opt_definitionALTER SUBSCRIPTION any_name SET definitionALTER SUBSCRIPTION any_name SET PUBLICATION publication_name_list opt_definitionALTER SUBSCRIPTION name RENAME TO nameALTER SYSTEMALTER SYSTEM RESETALTER TABLE [ IF EXISTS ] relation_expr RENAME CONSTRAINT name TO nameALTER TABLE [ IF EXISTS ] relation_expr RENAME opt_column name TO nameALTER TABLE [ IF EXISTS ] relation_expr SET SCHEMA nameALTER TABLE ALL IN TABLESPACE name OWNED BY role_list SET TABLESPACE name opt_nowaitALTER TABLE ALL IN TABLESPACE name SET TABLESPACE name opt_nowaitALTER TABLE <name> CLUSTER ON <indexname>ALTER TABLE <name> ALTER [COLUMN] <colname> RESET ( column_parameter = value [, … ] )ALTER TABLE <name> ALTER [COLUMN] <colname> SET ( column_parameter = value [, … ] )ALTER TABLE <name> ALTER [COLUMN] <colname> SET STORAGE <storagemode>ALTER TABLE <name> ALTER [COLUMN] <colname> SET STATISTICS <SignedIconst>ALTER TABLE <name> ALTER CONSTRAINT …ALTER TABLE <name> CLUSTER ON <indexname>ALTER TABLE <name> DISABLE RULE <rule>ALTER TABLE <name> ENABLE ALWAYS RULE <rule>ALTER TABLE <name> ENABLE REPLICA RULE <rule>ALTER TABLE <name> ENABLE RULE <rule>ALTER TABLE <name> INHERIT <parent>ALTER TABLE <name> NO INHERIT <parent>ALTER TABLE <name> NOT OFALTER TABLE <name> OF <type_name>ALTER TABLE <name> REPLICA IDENTITYALTER TABLE <name> RESET (…)ALTER TABLE <name> SET (…)ALTER TABLE <name> SET LOGGEDALTER TABLE <name> SET UNLOGGEDALTER TABLE <name> SET WITH OIDSALTER TABLE <name> SET WITHOUT CLUSTERALTER TABLE <name> VALIDATE CONSTRAINT …ALTER TABLESPACE name RENAME TO nameALTER TABLESPACE name RESET reloptionsALTER TABLESPACE name SET reloptionsALTER TEXT SEARCHALTER TRIGGER name ON qualified_name DEPENDS ON EXTENSION nameALTER TYPE any_name alter_type_cmdsALTER TYPE any_name RENAME ATTRIBUTE name TO name opt_drop_behaviorALTER TYPE any_name RENAME TO nameALTER TYPE any_name SET SCHEMA nameALTER TYPE <name> ADD ATTRIBUTE <coldef> [RESTRICT|CASCADE]ALTER TYPE <name> ALTER ATTRIBUTE <attname> [SET DATA] TYPE <typename> [RESTRICT|CASCADE]ALTER TYPE <name> DROP ATTRIBUTE <attname> [RESTRICT|CASCADE]ALTER TYPE <name> DROP ATTRIBUTE IF EXISTS <attname> [RESTRICT|CASCADE]ALTER VIEW [ IF EXISTS ] qualified_name alter_table_cmdsALTER VIEW [ IF EXISTS ] qualified_name RENAME TO nameALTER VIEW [ IF EXISTS ] qualified_name SET SCHEMA name
CLUSTERCREATE:CREATE ACCESS METHODCREATE ASSERTION name CHECKCREATE COLLATION [ IF NOT EXISTS ] any_name definitionCREATE COLLATION [ IF NOT EXISTS ] any_name FROM any_nameCREATE CONVERSIONCREATE INDEX COLLATECREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLYCREATE OptNoLog MATERIALIZED VIEW [ IF NOT EXISTS ] create_mv_target AS SelectStmt opt_with_dataCREATE PUBLICATIONCREATE RECURSIVE VIEWCREATE STATISTICS [ IF NOT EXISTS ] any_nameCREATE SUBSCRIPTIONCREATE TABLE:CREATE TABLE any_name AS EXECUTE plan_name- The
INHERIT,LIKE,NO INHERIT, andUNLOGGEDoptions aren’t supported - The
EXCLUDEconstraint isn’t supported
CREATE TRIGGER REFERENCINGCREATE VIEW: the following options aren’t supported:WITH CHECK OPTIONWITH CASCADED CHECK OPTIONWITH LOCAL CHECK OPTION
CREATE / DROP:CREATE / DROP LANGUAGECREATE / DROP TRANSFORM
DEFFERABLEconstraint:CREATE CONSTRAINT TRIGGER name AFTER TriggerEvents ON qualified_name OptConstrFromTable ConstraintAttributeSpec FOR EACH ROW TriggerWhen EXECUTE FUNCTION_or_PROCEDURE func_name '(' TriggerFuncArgs ')'
DROP:- Doesn’t support dropping multiple objects
DROP ACCESS METHODDROP ASSERTION nameDROP COLLATIONDROP CONVERSIONDROP INDEX CONCURRENTLY [ IF EXISTS ] any_name_list opt_drop_behaviorDROP MATERIALIZED VIEWDROP PUBLICATIONDROP STATISTICSDROP SUBSCRIPTION [ IF EXISTS ] any_name opt_drop_behavior
FETCH: the following directions not supported:ABSOLUTE,BACKWARD,FIRST,LAST,PRIOR, andRELATIVEREINDEX:REINDEX reindex_target_multitable nameREINDEX reindex_target_type qualified_nameREINDEX '(' reindex_option_list ')' reindex_target_multitable nameREINDEX '(' reindex_option_list ')' reindex_target_type qualified_name
SECURITY LABEL:SECURITY LABEL opt_provider ON AGGREGATE aggregate_with_argtypesSECURITY LABEL opt_provider ON DOMAIN_P TypenameSECURITY LABEL opt_provider ON FUNCTION function_with_argtypesSECURITY LABEL opt_provider ON LARGE_P OBJECT_P NumericOnlySECURITY LABEL opt_provider ON PROCEDURE function_with_argtypesSECURITY LABEL opt_provider ON ROUTINE function_with_argtypesSECURITY LABEL opt_provider ON security_label_type_any_name any_nameSECURITY LABEL opt_provider ON security_label_type_name nameSECURITY LABEL opt_provider ON TYPE_P Typename
LOADLOCK TABLE any_name IN lockmode: the following lock modes aren’t supported:ACCESS EXCLUSIVEEXCLUSIVEROW EXCLUSIVEROW SHARESHARESHARE ROW EXCLUSIVESHARE UPDATE EXCLUSIVE
MOVEREFRESH MATERIALIZED VIEW opt_concurrently qualified_name opt_with_data- Transactions:
COMMIT PREPARED SconstPREPARE TRANSACTION SconstRELEASE ColIdRELEASE SAVEPOINT ColIdROLLBACK opt_transaction TO ColIdROLLBACK opt_transaction TO SAVEPOINT ColIdROLLBACK PREPARED SconstSAVEPOINT ColId
TRUNCATE:TRUNCATE: CONTINUE IDENTITYTRUNCATE: RESTART IDENTITY
WHERE CURRENT OF cursor_name